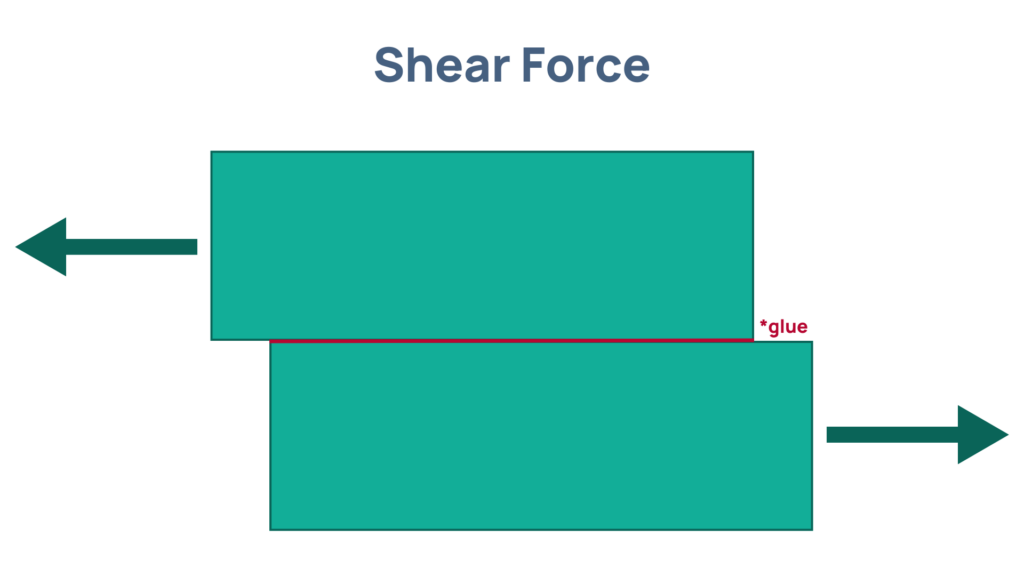
Shear forces occur when two opposing forces act parallel but in opposite directions, causing layers of material to slide past each other. In timber, shear strength is heavily influenced by grain direction. Shear parallel to the grain results in lower resistance and a higher risk of splitting along the grain, whereas shear perpendicular to the grain offers better strength.
Proper detailing and consideration of the grain direction are vital in elements subjected to shear forces, such as beams and connections.